

IT and The Marist Digital Vision
IT at The Marist and Our Digital Vision
21st Century Learning Skills are widely regarded as vital for all students. The world is changing rapidly, driven by technology and globalisation. To succeed in this new environment, students need to develop a new set of skills beyond traditional academic knowledge.
These skills, often referred to as 21st-century learning skills, include critical thinking, communication, collaboration, creativity, digital literacy, and global citizenship. These skills are crucial because they help students become adaptable, flexible, and innovative learners who can thrive in an ever-changing world. They also prepare them for the workforce, where employers increasingly demand employees who can work effectively in teams, solve complex problems, and use technology to their advantage.
Information Literacy
Information literacy refers to the ability to find, evaluate, use, and communicate information effectively and responsibly. This can refer to both print and digital information It is a critical skill in today’s information age, where we are bombarded with an overwhelming amount of data and need to distinguish reliable sources from unreliable ones. As part of our PSHCE curriculum in conjunction with the Learning Resources Centre students are taught information literacy skills.
Digital Literacy
Digital literacy refers to the ability to use digital tools and technologies effectively to find, evaluate, and create information. It involves a range of skills, including basic computer skills, information literacy, media literacy, and online safety. In today’s digital age, digital literacy is becoming increasingly important as technology plays a crucial role in our personal and professional lives.
Access to information: Digital literacy allows individuals to access and evaluate information from a variety of sources, including online databases, websites, and social media. It helps them to distinguish reliable sources of information from unreliable ones and make informed decisions.
Communication: Digital literacy allows individuals to communicate effectively using a variety of digital tools, including email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and social media. This facilitates collaboration and helps individuals to work more efficiently.
Employment: Digital literacy is increasingly important in the job market. Many jobs now require digital literacy skills, such as basic computer skills, online research, and social media proficiency. Digital literacy can help individuals to stand out in the job market and increase their employment prospects.
Creative expression: Digital literacy skills allow individuals to express their creativity using digital tools such as graphics software, video editing software, and social media. This enables individuals to create and share content with a wider audience.
Online safety: Digital literacy skills are essential for staying safe online. Individuals with digital literacy skills are able to identify and avoid online scams, protect their personal information, and use privacy settings to control their online presence.
Technology Skills
We need to ensure that pupils develop technology skills to be prepared for the demands of the modern workforce and to be successful in their personal and professional lives. These include:
Coding and programming: Coding and programming skills are becoming increasingly important in the modern workforce. Students should learn to code in languages such as Python or Java, and be able to create and test simple programs.
Multimedia skills: Students should be able to create and edit multimedia content, such as videos, images, and audio. They should understand how to use editing software, create visual content, and edit sound files.
Collaboration tools: Students should be proficient in using collaboration tools such as Shared Office Documents, Microsoft Teams, and email. These tools allow them to work collaboratively, communicate effectively, and share ideas.
Data analysis and visualization: As data becomes more important in many industries, students should develop skills in data analysis and visualization. They should be able to collect and analyse data, create charts and graphs, and interpret results.
Robotics and engineering: As automation and robotics become more prevalent, students should develop skills in robotics and engineering. They should be able to design and build robots, as well as understand the principles of automation and control.
Entry-level digital skills, meaning basic functional skills required to make basic use of digital devices and online applications, are widely considered a critical component of a new set of literacy skills in the digital era, with traditional reading, writing, and numeracy skills.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of machines and software to mimic human cognitive functions, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI has the potential to revolutionise the way we live and work, from self-driving cars to personalised healthcare, but it also presents new challenges and opportunities.
We believe pupils should learn how to use AI because it is rapidly becoming a critical part of our daily lives and has significant implications for their future careers. Understanding how AI works, its benefits and limitations, and how to use it responsibly and ethically is essential for students to thrive in a world that is increasingly shaped by technology.
By learning about AI, students can develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills that are essential for success in the 21st century. They can also learn how to use AI tools and applications to enhance their learning, streamline their workflows, and gain a competitive advantage in their future careers.
Student Laptops
As part of our drive to ensure our students are equipped for life in the 21st century we introduced laptops to Key Stage 3 students at the start of the 2021 – 2022 academic year. Staff and students received training in the use of both hardware and software. This year, nearly all year groups in the Senior School received laptops. The laptops were selected for a variety of reasons:
- typically offer more processing power, storage capacity, and memory, making them better suited for demanding tasks like video editing or programming.
- laptops have a physical keyboard are touch screen and come with a stylus to allow student to write or draw on the screen
- laptops have more ports and connectivity options, allowing users to easily connect to external devices like printers or monitors.
- laptops tend to have larger screens than tablets, providing a better viewing experience for movies, games, and other media.
- They are light enough but also hardwearing
- They have a rubberised casing to prevent knocks
- They run on Windows which is what most businesses use
- They can be opened 360 degrees to allow them to be used as a standard laptop or as a tablet
- They have a camera on both sides so they can be used in tablet mode to record video
There are many benefits to students having the same type of laptop and we find that it makes teaching far easier when all the students are using the same devices.
Blended Learning “Marist Style” combines the best of traditional teaching with the best of technology.
Digital devices and digital resources are used in lessons when they enhance a student’s learning experience, aid in accessing resources, or provide an opportunity for deeper learning.
Marist Maker Space
In September 2023 we introduced a “Marist Maker Space”. This is a hands-on space where students can tinker, create, program, design, 3D print, create robots, take things apart.
Encourages creativity and innovation: A maker space provides students with the opportunity to explore and experiment with their creativity and innovative ideas. They can collaborate with their peers and create solutions to real-world problems or pursue personal projects.
Develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills: A maker space encourages pupils to think critically and solve problems by giving them the freedom to experiment and try out new ideas.
Fosters collaboration and teamwork: A maker space encourages collaboration and teamwork, as pupils work together to brainstorm ideas, design and build projects, and share feedback, helping them develop important communication and teamwork skills.
Supports 21st-century learning: A maker space provides students with opportunities to develop 21st-century skills, such as creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration.
Provides hands-on learning experiences: Pupils can learn through trial and error, experiment with new technologies, and gain practical skills that can be applied in real-world situations.
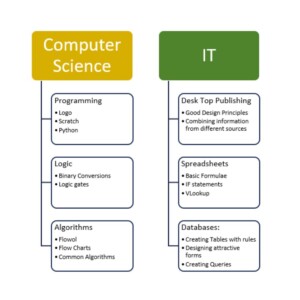
The Computer Science and IT Curriculum
Key Stage 3 Students all have 1 lesson of Computer Science a week where they cover a range of skills. We offer GCSE Computer Science, which is a popular choice. Currently we offer a 1 year AS in Computer Science but may expand this in future depending on demand.
We follow a two-strand approach to Computer Science, covering modules in both ICT and Computer Science. ICT (Information and Communication Technology) and computer science are two related but distinct fields.
ICT is a broad term that encompasses all forms of technology used to communicate and process information, including computers, mobile devices, and the internet. ICT focuses on how technology can be used to enhance communication, collaboration, and productivity.
Computer Science is a specific field of study that focuses on the design, development, and use of computer software and hardware. Computer science involves studying programming languages, algorithms, data structures, computer architecture, and artificial intelligence, among other topics. It is a more technical field than ICT, with a greater emphasis on software engineering, computer programming, and computer hardware design.
ICT is a broader field that focuses on the use of technology for communication and information processing, computer science is a more specialized field that deals specifically with computer software and hardware development and use.
Online Safety
Internet Safety Week is an annual event that promotes awareness and education about online safety and responsible digital citizenship. It typically takes place during the first week of February and is celebrated globally. During Internet Safety Week students take part in various activities and events to raise awareness about the risks of the online world, such as cyberbullying, identity theft, and online predators. The week aims to educate people on how to stay safe online, how to use the internet responsibly, and how to protect their personal information. It is an important initiative that helps promote safe and responsible internet use and encourages individuals to become more aware of the potential risks of the online world and to prepare pupils to be responsible and ethical digital citizens in the 21st century.
Parent Awareness
Internet Safety Week is an ideal opportunity for parents to get involved in their child’s online safety. During this week we offer various activities and resources to promote awareness and education about online safety. By getting involved in Internet Safety Week, parents can gain a better understanding of the potential risks and dangers of the online world and learn practical strategies to help their children stay safe online. Additionally, parents can use this week to have open and honest conversations with their children about online safety and work together to establish responsible digital habits and routines.


